Current issue
Online first
Archive
About the Journal
Aims and scope
Editorial Board
International Editorial Board
List of Reviewers
Abstracting and indexing
Ethical standards and procedures
REMV in Social Media
Contact
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Authors
Manuscript formatting template
Title page
Highlights
Payments
‘Ghostwriting’ and ‘Guestauthorship’
Guidelines for Referees
Why did housing prices rise to a record level in Turkey? An empirical analysis
1
Department of Economics, Kirikkale University, Turkey
2
Department of Economics, OSTIM Technical University, (Ministry of Trade of the Republic of Turkey), Turkey
Submission date: 2023-03-10
Final revision date: 2023-05-04
Acceptance date: 2023-05-31
Publication date: 2023-12-09
REMV; 2023;31(4):1-10
HIGHLIGHTS
- we retrospectively investigates the effect of Covid-19 pandemic and the changes in consumer confidence on housing prices and the volatility of housing prices
- we used the Lee and Strazicich structural break unit root test as a research method
- analysis period of the paper is 2010:q1-2022:q4 quarterly.
- the results show that economic policies and Covid-19 measures have been effective in increasing housing prices
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
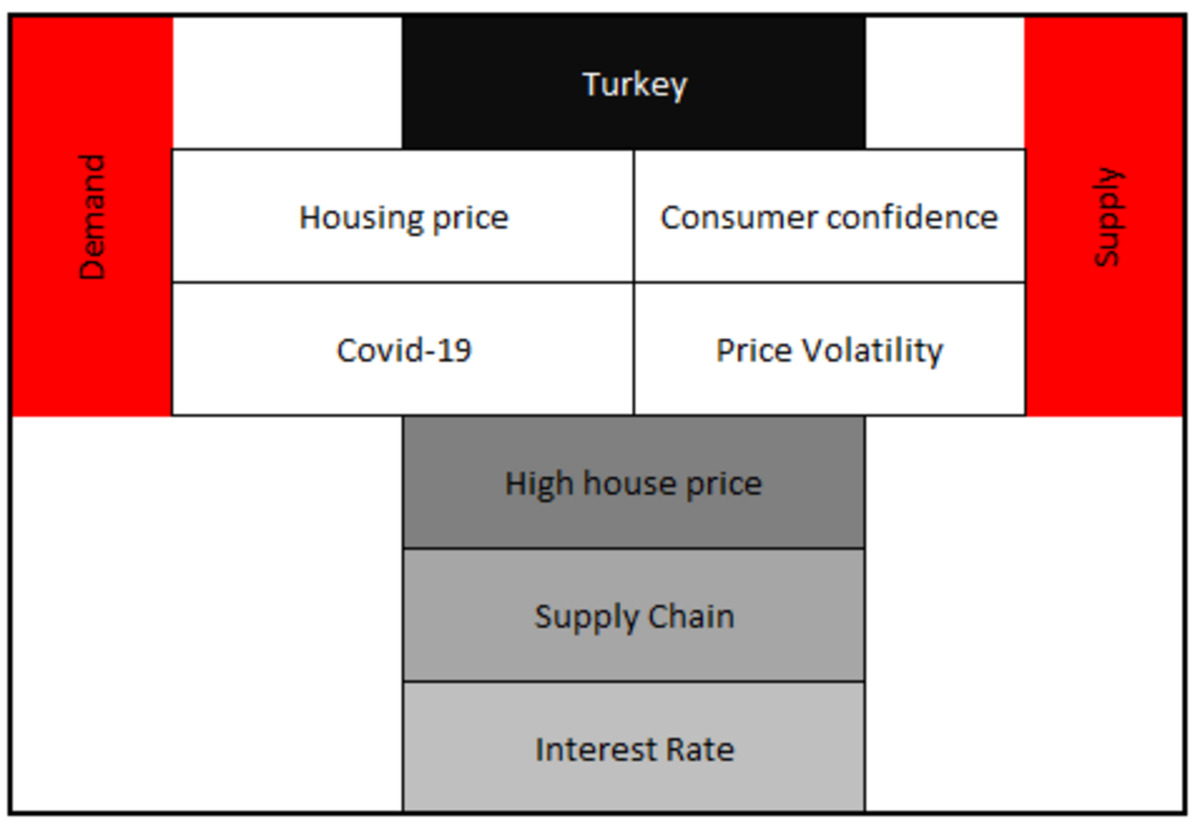
Turkey is one of those countries where housing market has been most severely affected by COVID-19 pandemic. Today the effects of the outbreak have been eliminated significantly. This study retrospectively looks at the days when the world faced a widespread outbreak of a pandemic and investigates the effect of the pandemic and the changes in consumer confidence on housing prices and the volatility of housing prices. Considering the structural breaks in the analysis period (2010:q1-2022:q4 quarterly), we used the Lee and Strazicich structural break unit root test as a research method. The results show that an increase in costs due to a break in the supply chain and containment measures forcing the workforce to stay at home affected the housing supply adversely. It is observable that expansionary economic policies and social assistance programs have a positive effect on housing demand. In this regard, negative supply shock and positive demand pressure are seen to be the determinants of the recent housing price increases in Turkey. However, while there is a positive relationship between consumer confidence and house prices, the effect of house prices on the volatility is statistically insignificant.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.