Current issue
Online first
Archive
About the Journal
Aims and scope
Editorial Board
International Editorial Board
List of Reviewers
Abstracting and indexing
Ethical standards and procedures
REMV in Social Media
Contact
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Authors
Manuscript formatting template
Title page
Highlights
Payments
‘Ghostwriting’ and ‘Guestauthorship’
Guidelines for Referees
Detecting abandoned houses in rural areas using multi-source data
1
Departament of Real Estate, Kangwon National University, Republic of Korea
Submission date: 2022-12-02
Final revision date: 2023-02-13
Acceptance date: 2023-02-23
Publication date: 2023-09-07
REMV; 2023;31(3):58-66
HIGHLIGHTS
- abandoned houses have become a common feature in rural areas over the past decade
- a cost-effective and prompt approach is investigated to detect abandoned houses
- images and building registry data are used in this study
- a multi-input neural network achieves 86.2% accuracy in detecting abandoned houses
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
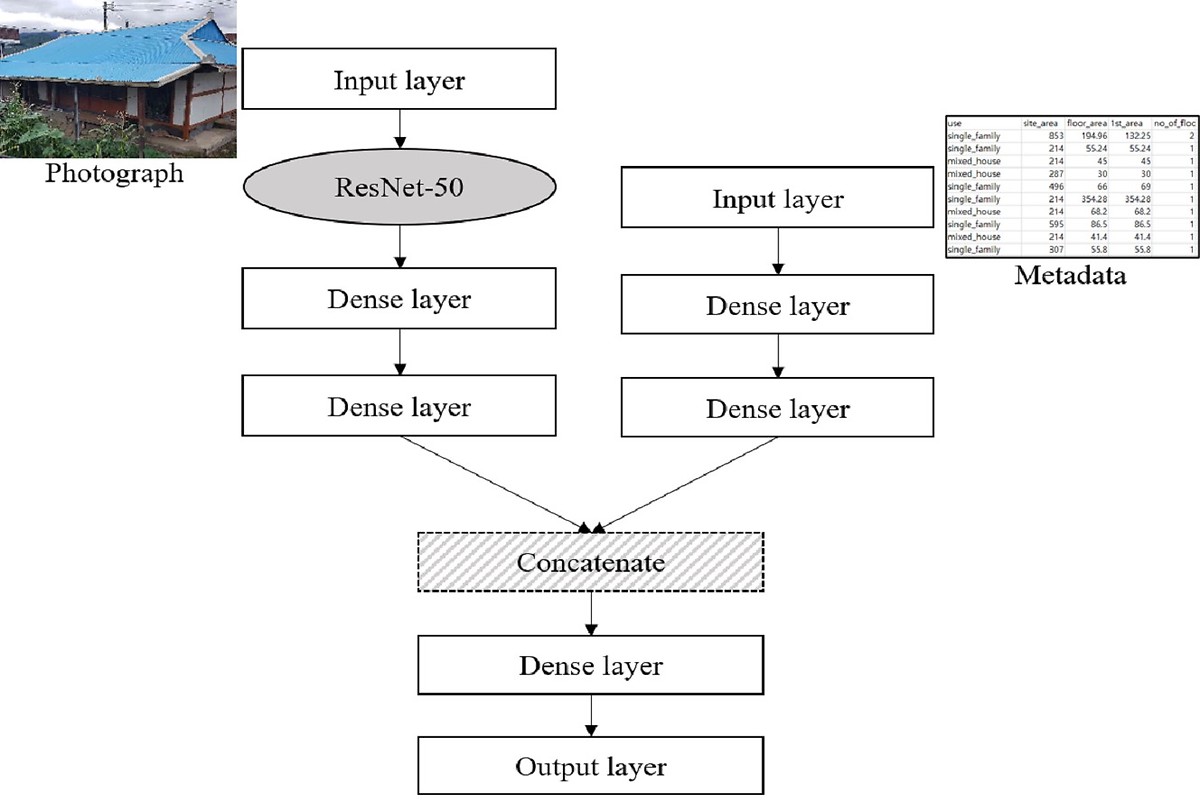
Abandoned houses have become a common feature of the local landscapes: the rising number of abandoned houses is a major challenge facing many counties in South Korea. Their presence negatively influences the neighborhood by undermining its aesthetic quality, depreciating the perception of safety in the neighborhood properties, and deepening the fiscal deficit of local financing. The detection of abandoned houses is the first step toward adequate housing management by local governments. This study aims to provide a cost-effective and prompt approach to identifying abandoned houses in rural areas. Multi-source data, that is, images and building registry data are utilized and a multi-input neural network is designed to adopt these heterogeneous datasets. Trained by the two source datasets, the proposed network achieves 86.2% accuracy in classifying abandoned houses, which is an acceptable performance level in administrative practice. The database of abandoned houses identified in this manner is expected to promote effective housing management by governments and ultimately contribute to mitigating vacancies in rural areas.
FUNDING
This study was supported by 2022 Research Grant from Kangwon National University.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.